


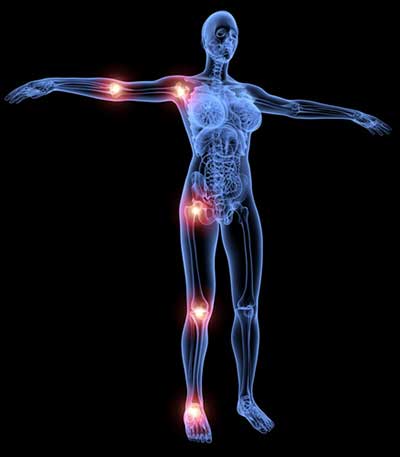
Fibromialgia, or fibromyalgia syndrome is a rheumatic disease which involves muscle skeletal system.
This disease shows several symptoms such as hyperalgesia meaning widespread chronic pain, muscle stiffness, weakness, insomnia, cephalea, gastrointestinal discomfort, memory difficulties and anxiety.
The latest Italian evaluation of fibromyalgia’s spread have estimated that it involves 2 million people especially women.
HOW TO RECOGNISE FIBROMYALGIA: CAUSES AND SYMPTOMS
The fibromyalgia patient seems healthy and serum and instrumental parameters are normal, no signs are visible on body.
This healthy appearance is not in according with the symptoms shown above and both diagnosis and therapy are slowed. The chronic pain evolves gradually and it leads disability but it is not degenerative.
The fibromyalgia pathogenesis is highly debated and it inspires distrust in medical community. In according with the latest studies the multifactorial theory is mostly followed and neurotransmitters and hormonal impairment, caused by traumatic events, together with genetic susceptibility, are considerate the trigger of fibromyalgia.
Typical symptoms are shooting widespread pain which is able to interfere with daily activities, single or wide spread muscle pain are common as well as joint, tendon and ligament stiffness. In addiction weakness, fatigue, anxiety, depression, insomnia, cognitive and memory loss, urinary diseases, dysmenorrhea, chronic headache, gastrointestinal discomfort. These symptoms lead to impairment of the quality of sleep and life.


HOW TO GET TO FIBROMYALGIA DIAGNOSIS
The Fibromyalgia is a rheumatic disease and it requires a specialist to be diagnosed. The diagnosis is based on exclusion of other rheumatic diseases through serum and instrumental tests. In particular the patient’s medical history and clinical data are fundamental to diagnosis. The causes of fibromyalgia are multiple as biochemicals, genetic or environmental factors.
Some years ago a basic role to lead to fibromyalgia diagnosis were tender points. These were tendon or muscle points distributed along the body which were painful under pressing. Based on American College of Rheumatologist’s map there were 18 tender points. During the medical check if more than half of the tender points were positive to the press the diagnosis was fibromyalgia. Today the diagnosis is based on the exclusion of other rheumatic diseases together with the use of medical fibromyalgia questionnaire (questions and answers). The final score of this questionnaire sets out the fibromyalgia diagnosis.
To lead to fibromyalgia diagnosis three criteria must be fulfilled:
Symptoms are measured by Fibromyalgia Severity Scale, and the score includes:

Concerning wide spread pain the maximum score is 19, instead for severity symptom it is 12. The fibromyalgia diagnosis is confirmed by a score >=12 of Fibromyalgia Severity Scale, which is composed of:
Wolfe et al. (2016) confirmed that the fibromyalgia diagnosis does not exclude other relevant clinical disturbances.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis is complex in the context of the wide number of rheumatic diseases together with other signs or symptoms in common to fibromyalgia. The exclusion of other rheumatic diseases is obtained by meticulous anamnesis physical examination and a set of laboratory tests or x-ray (fibromyalgia does not have a specific laboratory or instrumental parameters to be tested).
The recommended laboratory tests are:
Concerning instrumental tests there are no recommendations from the international medical community.
The most important diseases to base differential diagnosis are: rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus, rheumatic polymyalgia, polymyositis, spondyloarthritis, hyperparathyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, neuropathy.
FIBROMYALGIA: PHARMACEUTICAL THERAPY
Fibromyalgia is linked to the pain processing: pain is amplified or its inhibition is reduced. On the base of this disease there is an impairment of neurochemical balance involved with “neuronal talking”, it causes a neuro-psychological symptomatology. For this reason a therapy based on anti-inflammatory or analgesic drugs is ineffective. The fibromyalgia therapy is based on muscle relaxers, or tricyclic antidepressant, benzodiazepine, anticonvulsant, taken at low doses under medical control. These drugs are effective in pain reduction, muscle spasms, sleeping or mood disturbances, but they are ineffective on physical tiredness and mental fatigue.

One of the most common symptoms in fibromyalgia is lack of concentration and memory. These patients report a mental fog (fibro fog) which affects the daily life and work. In addition to conventional drugs, the adjuvant therapy can include energetic food supplements. The synergistic effects of micronutrients, vitamins and minerals can help to relieve physical tiredness, mental fatigue and “fibro fog”.
Natural food supplement and phytotherapy preserve nervous functions and immune system. In addition positive effects have been reported on sleeping disturbances, mental and physical recovery. All fibromyalgia studies have shown therapeutic improvements with a combination of drugs, food supplements, low impact aerobic activity and cognitive-behavioral therapy. This approach helps to comprehend the disease ant it stimulates a normal coexistence with it. Finally healthy lifestyle, natural diet, caffeine intake reduction, inflammatory food avoidance, play an important role in fibromyalgia’s symptoms control.
Fibromyalgia is a complex disease which causes wide spread chronic pain, especially charged to muscles and joints, in addiction to fatigue, weakness, sleeping disturbance, gastrointestinal discomfort, and depression. This causes a deterioration of the quality of life.
The estimated fibromyalgia spread in Italy is 2.2-3.7% of general population and 5.5% of female population with 1, 5-2 million people affected.
The latest guidelines for the fibromyalgia treatment propose a “soft approach” based on physical activity and stretching as first therapeutic guidance, vice versa drugs therapy is subsequently introduced on the base on patient’s needs.
Recommended drugs for treating pain are Duloxetine, Pregabalin, Tramadol even combined with Paracetamol; Cyclobenzaprine or Pregabalin are recommended at low doses to treat sleeping disturbances.
In addition the therapy includes physical activity, cognitive behavioural therapy and psychological support, while a food supplement could be suggested to improve fatigue, weakness, and fibro fog.
A multidisciplinary medical, physical and psychological approach is essential to lead the patient to a better quality of life.
Conventional drugs could not improve the fibromyalgia pain. It is estimated that a substantial pain reduction (from 50% onward) is achieved in 10-25% of patients (Moore A. et Al, 2013). The fibromyalgia pain seems to be not different from other chronic pain, but the data shows that only a small part of these patients are responsive to conventional anti pain drugs. Doctors are questioning if cannabis could be used in no responders patients. Currently the scientific literature shows that Nabilone (synthetic cannabinoid included in medical approved drug list) has enough studies to be examined as fibromyalgia therapy. Vice versa there are not enough studies to evaluate the medical use of plant cannabis. However a self-use is not recommended because of the quality-quantity lacking control on active substance. The authors of this authoritative study conclude that the review of the references leads not to recommend the use of Nabilone in the fibromyalgia treatment in addition the authors highlight that the compliance of this drug is poor. The hope for the future is for other cannabinoids and alternative administration as the new patch based on THC precursor (ZYN001 precursor of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) currently under study.


